Disaster Risk Management (DRM)
Understanding Disaster Risk Management
This module aims at builds on previous sessions outlining a number of concepts and terms that are used in Disaster Risk Management. This will provide a basis for effective understanding of these terminologies and the concepts. It also tackles issues to do with Disaster Risk Management (DRM) cycle focusing on all the stages of the cycle that include pre-disaster, Response and post-disaster. It is important therefore, to understand these concepts and the DRM cycle.
Specific Objectives : At the end of this module participants will be able to: To discuss stages in the DRM Cycle
Step2: Divide the participants into groups
Step 3: Paste the following words on the wall visible to all: Means of Livelihood, Vulnerability, Capacity, Disaster Risk, Prevention, Disaster, Disaster Risk Management, Disaster Risk Reduction, Resilience, Mitigation, etc
Step 4: Give each group meanings of the pasted words and ask them to discuss the meanings one by one once they agree they should paste the meaning under that word (paste it in the way that no one can read until all groups have pasted).
Step 5: Once all groups have finished pasting ask all participants to come close to the pasted words and meanings.
Step 6: A volunteer should turn the meanings making them visible to all and should read all the meaning pasted by the groups under that word. Ask the participants if it is the right meaning of the word and if it is not the right meaning take it off.
Step 7: At the end the facilitator to summarise and give right definitions accordingly using practical examples.
Step 8: Then the facilitator asks participants to brainstorm if at all they know stages of Disaster Risk Management cycle.
Step 9: After brainstorming, the facilitator to give the three stages of DRM cycle and explain the meaning of each stage.
Step 10: Divide participants into three groups and assign one stage per group and ask the groups to suggest activities for each stage and present in plenary.
Step 11: After plenary, the facilitator to beef up the discussions by showing the DRM cycle and explain each stage and the associated activities.
The Disaster Risk Management Process:
This provides an in depth understanding of 3 main stages in Disaster Risk Management as detailed in the figure below
The DRM Cycle
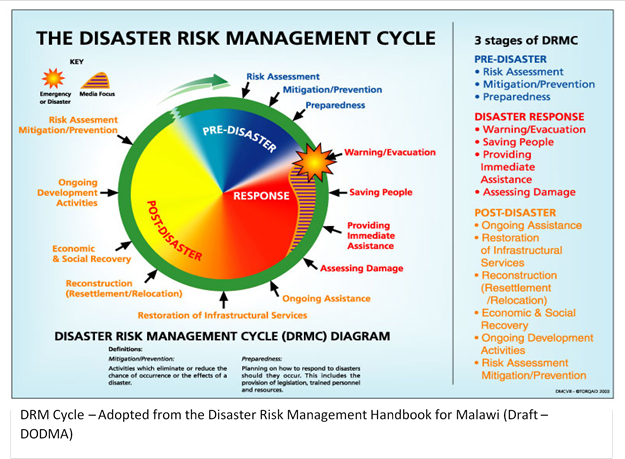
The disaster risk management cycle is a continuous process by which governments, development partners, private sector, civil society and communities plan for and reduce the impact of disasters, react during and immediately following a disaster, and take steps to recover after a disaster has occurred. In other words, DRM consist of both Disaster Management (the traditional preparedness, response and recovery activities) as well as Disaster Risk Reduction (prevention and mitigation) (DRM Handbook, DODMA)
In the pre-disaster phase activities including risk assessment, implementation of mitigation measures and preparedness are undertaken. After disasters have occurred, the phase is now called a response phase. During this phase, different activities depending on the nature of the disaster will take place including evacuation, providing immediate assistance, assessing damage and re-evaluation adequacy of assistance while providing it. This phase then moves into the post disaster phase, which is the third and final stage. As indicated earlier, the speed at which phases change is dependent on the nature and the intensity of the disaster.
The DRM cycle simplifies the sequence of activities as a conceptual tool only. For example, mitigation and/or prevention efforts undertaken this year may not have impact on the hazards this year but five years down the line as in reafforestation projects.
- PRE-DISASTER
This involves three main activities and that’s:
- Risk Assessment- Under this, Risks are identified, analysed and interpreted. The most common questions asked include:
- What is the Risk(i.e. Disaster)
- Why is it a Risk (i.e. what means of livelihood will be affected)
- Who is at Risk (i.e. population group)
- Where (i.e. Location)
- Mitigation and prevention measures-Under Prevention measures that ensure that an event does not occur or does not negatively impact a community are implemented. While under sustained actions that reduces or eliminates long term risk to people and property from natural hazards and their effects are implemented. The Common Question asked under this include:
- What can we do to avoid the disaster occurrence
- What are the resources
- Who will supply the resources
- Preparedness- Under this measures to organise and facilitate search, rescue, relief and rehabilitation are implemented. Common questions that are asked include:
- What plans should we have (i.e. disaster plans, contingency plan)
- What skills our volunteers needs (i.e. Training of Volunteers)
- Whom will we work with (i.e. Forming partnership)
- What should we keep and How much ( i.e. stock piling o supplies)

- Early warning-Under this a systematic collection and analysis of information coming from areas of hazards/disasters for the purpose of anticipating the escalation of life threatening situations, the development of strategic responses to these situations and the presentation of options to critical stakeholders for purpose of decision making is done .It also involves disseminating the right information through the right channel to the right people at the right time hence making the people ready/ get prepared to a hazard that is to occur therefore lowering the risk and preventing disaster. Common questions that are asked include:
- When will it end ( on-going)
- Why do we need it ( i.e. timely response to disasters, timely information to possible
Trigger events and activation of contingency plans)
- How complex ( easier to do for slow onset disasters)
- Every hazard has its own early warning signs
- Locally developed signs are to be promoted based on their usefulness and efficiency
- DISASTER

Under this the main activity is response which involves the following:
- Saving people-Under this, saving lives activities are implemented and the aim is to rescue those that has been hit by a disaster. Activities done include:
- Search and rescue
- Disaster assessment- This is done by VCPC or ACPC
- Verification-this is done by DCPC whereby report from ACPCs is verified
- Reporting-Disaster reports must be written BUT if a disaster is of fast setting an oral report can be submitted first followed by a written report. Remember that a Disaster Report that is being submitted to the DC must be signed and stamped by the T/A
- Providing immediate Assistance- This involves providing the most essential basic requirements to the affected households. These can be inform of :
- Food (wet or dry rations)
- Shelter (i.e. tents, plastic sheets)
- Clothes
- Safe and secure environment
- POST DISASTER
- Restoration of Infrastructure Services- After a disaster has occurred many services may suffer i.e. education services may suffer because schools might be used as temporally shelter sites for displaced people.
- Reconstruction- Under this is where the affected households are assisted in reconstruction of resistant infrastructures. The common questions that are asked include:
- What to construct (i.e. houses, bridges, food storage facilities, roads)
- With what resources (i.e. locally or externally sourced or both)
- How strong or safe (i.e. flood and strong wind resilient houses based on risks associated with that particular area)
- Economic and Social Recovery- Disasters are normally associated with loss of both economic and social entitlement hence under this is where communities are economically empowered and also socially united. The most common question that are asked include:
- What are the economic needs ( i.e. business ideas, types of businesses)
- What are the economic opportunities available (i.e. business opportunities)
- With what resources can economic breakthroughs be realised ( i.e. resources needed)
- Ongoing Development Activities- Under this sustainable socio-economic activities are promoted in the disaster affected area
